

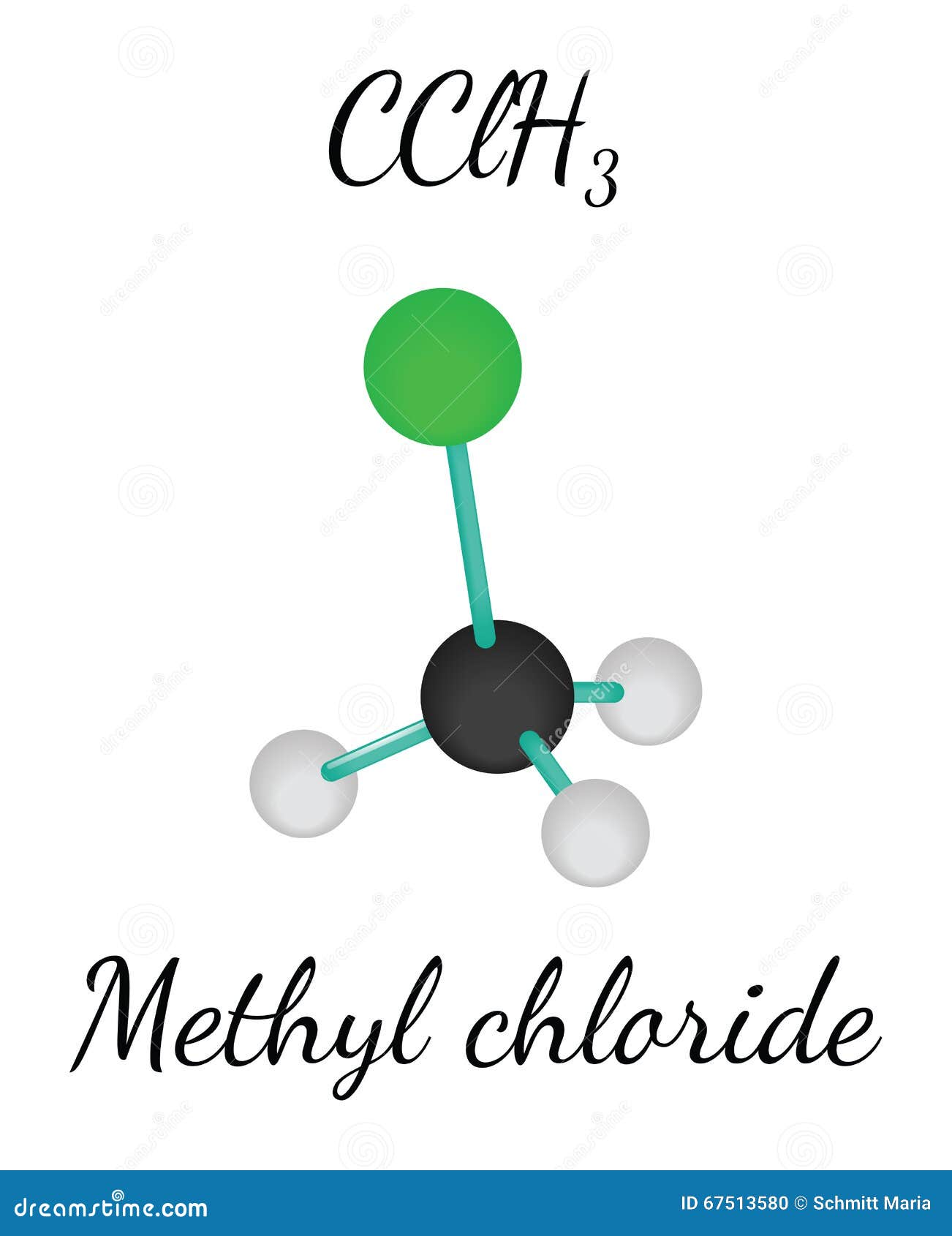
Chlorine is a component with mercury in the sulfate mineral kleinite. It appears with copper in the sulfate mineral connellite. Chlorine appears with copper in atacamite.Ĭhlorine appears in the phosphate mineral chlorapatite. Chlorine is in the lead-containing carbonate mineral phosgenite. Chlorine atoms react with a variety of organic molecules by abstraction of an H atom, making HCl and a radical co-product, and investigations of these. Other lead-containing chloride minerals are boleite, cumengite and laurionite. Chlorine has electronic configuration Ne 3s 2 3p 5 with the seven electrons in the third outermost shell acting as its valence electrons. Chlorine is the second member of halogen group it has similar properties like fluorine, bromine and iodine. Lead with chlorine and fluorine form matlockite. Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and it has atomic number 17. A chloride of lead and antimony is nadorite, PbSbO 2Cl.
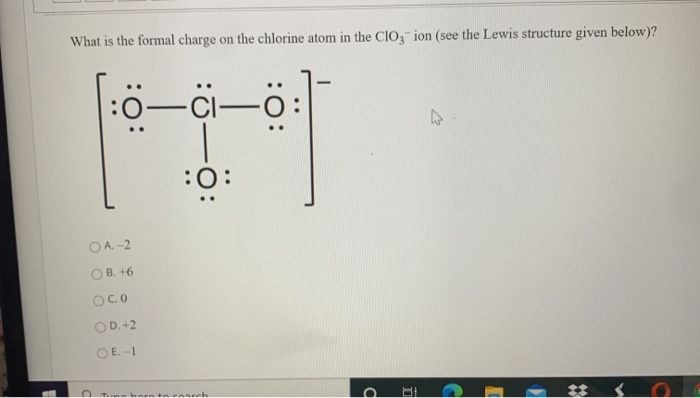
A chloride of copper and lead is diaboleite.

From simple clear ionic crystals like halite, NaCl, to more complex halide containing minerals like the yellow crystals of mimetite, Pb 5(AsO 4) 3Cl, chlorides show a range of colors.One lead chloride mineral is mendipite, PbO 2Cl 2. This forms hydrochloric acid, a very strong acid.Ĭhlorine is a constituent of many mineral crystals. The gas dissolves readily in water with the liberation of heat. Chlorine is a toxic, corrosive, greenish yellow gas that is irritating to the eyes and to the respiratory system. Hydrogen chloride, HCl, is a gas with a sharp unpleasant odor. chlorine chlorine (Cl), chemical element, the second lightest member of the halogen elements, or Group 17 (Group VIIa) of the periodic table. So, based on the shell, the electronic configuration of the Chlorine atom is 2, 8, 7. From the Bohr model of Chlorine, we know, that 2 electrons are in the K-shell, 8 electrons are in the L-shell, and 7 electrons are in the M-shell. This has led to widespread use in the sterilization of drinking water, for swimming pools, etc. Chlorine has an atomic number of 17 and it contains a total number of 17 electrons. It is manufactured on a large scale by electrolysis of concentrated solutions of sodium chloride.Ĭhlorine is a strong oxidizing agent and as a result is effective in killing bacteria. In pure form, it is a greenish-yellow gas with a sharp, irritating odor. It is not as chemically active as fluorine, but is still very active and forms compounds with most elements. Since the question states that there are 17. Phenom., 1980, 21, 275.Chlorine is the most common of the halogens. This is because the atomic number equals the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. Mårtensson, "Core-Level Binding Energies in Metals," J. Lide, (Ed.) in Chemical Rubber Company handbook of chemistry and physics, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, USA, 81st edition, 2000. Ley, Eds., Photoemission in Solids I: General Principles (Springer-Verlag, Berlin) with additional corrections, 1978. Burr, "Reevaluation of X-Ray Atomic Energy Levels," Rev. They are tabulated elsewhere on the WWW (reference 4) and in paper form (reference 5). The data are adapted from references 1-3. I am grateful to Gwyn Williams (Jefferson Laboratory, Virginia, USA) who provided the electron binding energy data. The binding energies are quoted relative to the vacuum level for rare gases and H 2, N 2, O 2, F 2, and Cl 2 molecules relative to the Fermi level for metals and relative to the top of the valence band for semiconductors. All values of electron binding energies are given in eV. 1967, 47, 1300.Įlectron binding energies Electron binding energies for chlorine. These effective nuclear charges, Z eff, are adapted from the following references: 10:42 Joining atoms together Chemical bonds The gases in the last column of the periodic table. The rest consists of a positively charged nucleus of protons and neutrons surrounded by a. As such, the atom is the basic building block of chemistry. It also is the smallest unit of matter that has the characteristic properties of a chemical element. Effective nuclear charges for chlorine 1s atom, smallest unit into which matter can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
